Basic Identities Closure Property of Addition

Closure Property of Multiplication
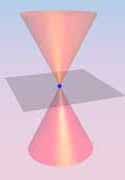
By changing the angle and location of intersection, we can produce a circle, ellipse, parabola or hyperbola; or in the special case when the plane touches the vertex: a point, line or 2 intersecting lines.
The type of section can be found from the sign of: B2 - 4AC
The Conic Sections. For any of the below with a center (j, k) instead of (0, 0), replace each x term with (x-j) and each y term with (y-k).
Sum (or difference) of 2 real numbers equals a real numberAdditive Identity
a + 0 = aAdditive Inverse
a + (-a) = 0Associative of Addition
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)Commutative of Addition
a + b = b + aDefinition of Subtraction
a - b = a + (-b)
Closure Property of Multiplication
Product (or quotient if denominatorMultiplicative Identity0) of 2 reals equals a real number
a * 1 = aMultiplicative Inverse
a * (1/a) = 1 (a(Multiplication times 0)0)
a * 0 = 0Associative of Multiplication
(a * b) * c = a * (b * c)Commutative of Multiplication
a * b = b * aDistributive Law
a(b + c) = ab + acDefinition of Division
a / b = a(1/b) Conic Sections
| Conic Sections |
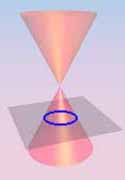 | 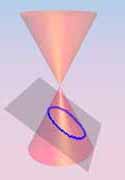 | 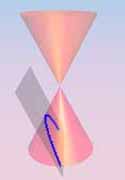 | 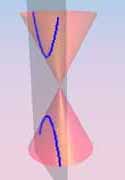 |
Circle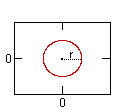 | Ellipse (h)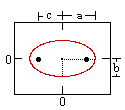 | Parabola (h)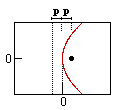 | Hyperbola (h)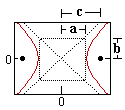 |
| Definition: A conic section is the intersection of a plane and a cone. | Ellipse (v)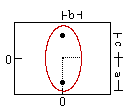 | Parabola (v)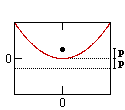 | Hyperbola (v)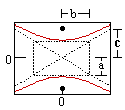 |
By changing the angle and location of intersection, we can produce a circle, ellipse, parabola or hyperbola; or in the special case when the plane touches the vertex: a point, line or 2 intersecting lines.
 | 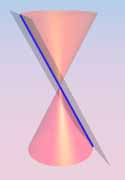 | 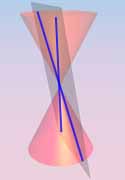 |
Point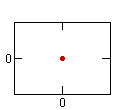 | Line | Double Line |
| The General Equation for a Conic Section: Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0 |
| If B2 - 4AC is... | then the curve is a... |
| < 0 | ellipse, circle, point or no curve. |
| = 0 | parabola, 2 parallel lines, 1 line or no curve. |
| > 0 | hyperbola or 2 intersecting lines. |
| Circle | Ellipse | Parabola | Hyperbola | |
| Equation (horiz. vertex): | x2 + y2 = r2 | x2 / a2 + y2/ b2 = 1 | 4px = y2 | x2 / a2 - y2 / b2= 1 |
| Equations of Asymptotes: | y = ± (b/a)x | |||
| Equation (vert. vertex): | x2 + y2 = r2 | y2 / a2 + x2/ b2 = 1 | 4py = x2 | y2 / a2 - x2 / b2= 1 |
| Equations of Asymptotes: | x = ± (b/a)y | |||
| Variables: | r = circle radius | a = major radius (= 1/2 length major axis) b = minor radius (= 1/2 length minor axis) c = distance center to focus | p = distance from vertex to focus (or directrix) | a = 1/2 length major axis b = 1/2 length minor axis c = distance center to focus |
| Eccentricity: | 0 | c/a | 1 | c/a |
| Relation to Focus: | p = 0 | a2 - b2 = c2 | p = p | a2 + b2 = c2 |
| Definition: is the locus of all points which meet the condition... | distance to the origin is constant | sum of distances to each focus is constant | distance to focus = distance to directrix | difference between distances to each foci is constant |
| Related Topics: | Geometry section on Circles |
(a+b) 2 = a 2 + 2ab + b 2 (a+b)(c+d) = ac + ad + bc + bd a 2 - b 2 = (a+b)(a-b) (Difference of squares) a 3 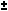 b 3 = (a b 3 = (a 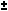 b)(a 2 b)(a 2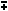 ab + b 2) (Sum and Difference of Cubes) ab + b 2) (Sum and Difference of Cubes)x 2 + (a+b)x + AB = (x + a)(x + b)if ax 2 + bx + c = 0 then x = ( -b 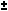 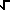 (b 2 - 4ac) ) / 2a (Quadratic Formula) (b 2 - 4ac) ) / 2a (Quadratic Formula)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
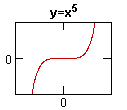
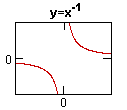
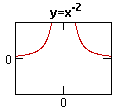
No comments:
Post a Comment